Gardenia Fruit Zhi Zi: Clearing Heat, Calming Mind, and Detoxifying in Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Health Lab

- Jun 5, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Jun 17, 2025
Gardenia fruit, also known as Zhi Zi or Cape Jasmine fruit, is the dried, mature fruit of the gardenia plant from the Rubiaceae family. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), it is valued for its ability to clear heat, reduce irritability, and detoxify the body. This article explains the properties, uses, and modern research on gardenia fruit in a simple and clear way.
Gardenia fruit has been used in TCM for centuries. Its earliest record appears in the Shennong Bencao Jing (Shennong’s Classic of Herbal Medicine), where it is listed as a mid-grade herb. The text describes it as a remedy for internal imbalances, stomach heat, yellowish skin, and skin sores.
Over time, Chinese physicians like Li Shizhen in the Ming Dynasty detailed its uses in the Compendium of Materia Medica, noting its ability to clear heat from the heart, lungs, and triple burner (a TCM concept) and promote digestion.
Properties of Gardenia Fruit
Nature and Flavor
Taste: Bitter
Nature: Cold
Meridians: Heart, lung, and triple burner
Main Components
Gardenia fruit contains geniposide and crocin, which contribute to its unique health benefits.
Key Benefits
Reduces irritability and calms the mind
Clears heat and promotes urination
Cools the blood and detoxifies
Relieves jaundice
Soothes mouth sores and oral ulcers
Pharmacological Effects
Modern studies suggest gardenia fruit has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, bile-promoting, and calming properties. It also helps lower blood pressure.

Clinical Uses of Gardenia Fruit
Gardenia fruit is widely used in TCM to treat various conditions:
Reducing Irritability: It clears heart fire, calming restlessness, insomnia, and mouth sores caused by excessive internal heat.
Clearing Heat and Dampness: It helps with jaundice, scanty or painful urination, and other symptoms caused by damp-heat accumulation.
Cooling Blood and Detoxifying: It treats bleeding issues like nosebleeds, vomiting blood, or blood in urine due to blood heat, as well as toxic skin sores.
Jaundice Relief: It promotes bile flow, helping reduce jaundice symptoms.
Mouth Sore Relief: It soothes oral ulcers and mouth sores caused by excessive heart fire.

Gardenia Fruit in Classic TCM Formulas
Gardenia fruit is often combined with other herbs in TCM formulas to enhance its effects. Here are some examples:
Zhi Zi Chi Tang (Gardenia and Fermented Soybean Decoction):
Ingredients: Gardenia fruit, fermented soybean
Benefits: Clears heat and relieves irritability, used for fever, insomnia, and restlessness after illness
Yin Chen Hao Tang (Capillaris Decoction):
Ingredients: Capillaris, gardenia fruit, rhubarb
Benefits: Clears heat, removes dampness, and reduces jaundice
Xie Xin Tang (Drain the Heart Decoction):
Ingredients: Rhubarb, coptis, scutellaria, gardenia fruit
Benefits: Clears heat and detoxifies, used for heat-related conditions
Comparison with Similar Herbs
Gardenia fruit shares benefits with other TCM herbs but has unique qualities:
Coptis (Huang Lian): Clears heat and dampness, but its bitter-cold nature is stronger, making it better for severe damp-heat conditions.
Scutellaria (Huang Qin): Clears heat and dampness, particularly in the upper body, and is often used for lung-related issues like cough.
Gentiana (Long Dan Cao): Clears heat and dampness, especially liver and gallbladder fire, but is less focused on heart fire compared to gardenia fruit.
Modern Applications and Research
Recent studies have highlighted gardenia fruit’s potential in modern medicine:
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Geniposide reduces inflammation by inhibiting inflammatory mediators.
Antibacterial Effects: It inhibits various bacteria and fungi.
Bile Promotion: It supports bile secretion, aiding digestion.
Calming Effects: It reduces nervous system activity, promoting relaxation and sleep.
Blood Pressure Reduction: It helps lower blood pressure.
Gardenia fruit is used today to support treatments for infections, inflammation, high blood pressure, insomnia, anxiety, and hepatitis. It shows promise in managing various health conditions.
How to Use Gardenia Fruit Safely
Dosage
Typical dose: 6–12 grams, as prescribed by a TCM practitioner.
Precautions
Avoid in cases of weak digestion or spleen-stomach deficiency with cold.
No specific herb combination restrictions are noted.
Preparation
Boil in a decoction or grind into powder for external use.
Selection Tips
Choose fruits that are dry, intact, and free of impurities.
Conclusion
Gardenia fruit is a powerful herb in TCM, valued for its ability to clear heat, calm irritability, reduce jaundice, and detoxify the body. Its long history and modern research highlight its potential in both traditional and contemporary medicine. However, it should be used under professional guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness. As research continues, gardenia fruit’s role in health and wellness is likely to expand.
Chinese Name | 梔子 |
Chinese Pinyin | Zhizi |
English Name | Common Gardenia Fruit |
Latin Pharmaceutical Name | Gardeniae Fructus |
Category | Fruits and seeds |
Origin | The dried mature fruit of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis. (Rubiaceae) |
Production Regions | Primarily produced in the Chinese provinces of Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Fujian. |
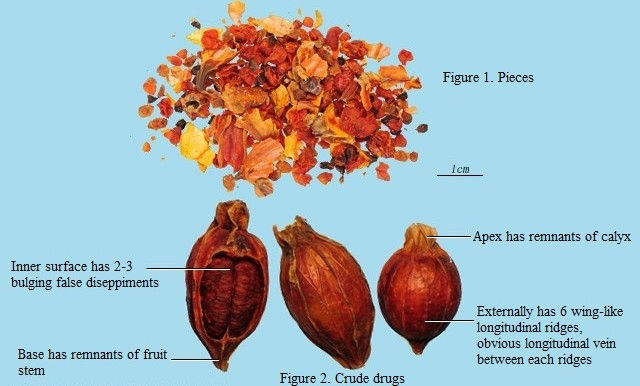
Macroscopic Features | Inverse oval, elliptical or long elliptical shape, 1.4~3.5cm long, 0.8~1.8cm diameter. Externally reddish-brown or reddish-yellow, slightly lustrous, with 6-8 wing-like longitudinal ridges, with one longitudinal vein between every 2 ridges, apex has dark yellowish-green remnants of persistent calyx, with 6-8 long lobes, lobes are 1~2.5cm long, 2~3mm wide, often crushed, fruit base shrunken and stem-like, end has round stem scar. Fruit skin is thin and brittle, inner surface is fresh yellow or reddish-yellow. Lustrous, with 2~3 bulging pseudoseptums. Fractured surface is fresh yellow, numerous seeds, flat oval or flat rectangular shape, clustered into spherical lumps, brownish-red, externally has thin and dense indented small spots; endosperm is horn-like; embryo is long, with 2 heart-like cotyledons. faint odor, slightly sour and bitter taste. |
Quality Requirements | Superior medicinal material has thin skin, full, reddish-yellow color. |
Properties | Bitter, cold. |
Functions | Drains fire, eliminates vexation, clears heat, promotes urination, cools blood, resolves toxin. Apply to deficient restlessness due to pyreticosis, conjunctival congestion due to liver fire, headache, jaundice due to damp-heat, strangury, hematodiarrhoea, hematuria, mouth and tongue sore, swelling pain of sore and ulcer, swelling pains caused by sprains. |
Processed Form | Fried zhi zi: Mashed zhizi fried with slow fire until turn into golden-yellow, take out and cool. Moderate the nature of unprocessed medicinal material. Burnt zhi zi: mashed zhizi fried with fast fire until turn into burnt color, take out and cool. Change the physical feature of hardness of zhi zhi, easily to boil. Zhi zi charcoal: mashed zhizi fried with fast fire until turn into black-brown, but save its nature, take out and cool. Focus on the effect of cooling blood and stopping bleeding, apply to hematemesis due to blood heat, epistaxis and hematuria, metrorrhagia and metrostaxis. |



Comments